Public Key authentication for SSH - improve security, enable automatic log in without passwords.
-->With a secure shell (SSH) key pair, you can create virtual machines (VMs) in Azure that use SSH keys for authentication. This article shows you how to quickly generate and use an SSH public-private key file pair for Linux VMs. You can complete these steps with the Azure Cloud Shell, a macOS or Linux host.
- Password - Extract public/private key from PKCS12 file for later use in SSH-PK-Authentication.
- 16 hours ago ssh -p 2222 root@193.xx.xx.xx -L 5432:127.0.0.1:5432 Due to a security upgrade, the guys at the remote said the port mapping has been deleted and asked for my ssh pub key so they give me access. But then I added other ssh keys, so I cannot tell which key is for this remote server.
- Configuring SSH to use Key Based Authentication. To copy the public key into the remote server, you can simply manually copy the key to remote server.
Note
VMs created using SSH keys are by default configured with passwords disabled, which greatly increases the difficulty of brute-force guessing attacks.
For more background and examples, see Detailed steps to create SSH key pairs.
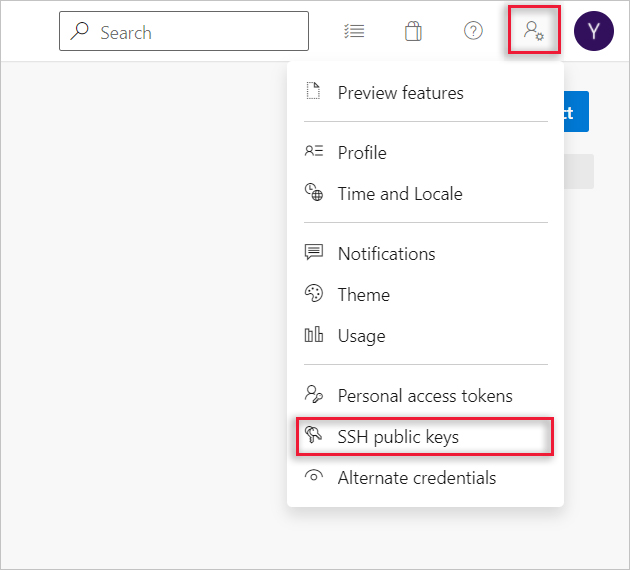
For additional ways to generate and use SSH keys on a Windows computer, see How to use SSH keys with Windows on Azure.
Supported SSH key formats
Azure currently supports SSH protocol 2 (SSH-2) RSA public-private key pairs with a minimum length of 2048 bits. Other key formats such as ED25519 and ECDSA are not supported.
Create an SSH key pair
Use the ssh-keygen command to generate SSH public and private key files. By default, these files are created in the ~/.ssh directory. You can specify a different location, and an optional password (passphrase) to access the private key file. If an SSH key pair with the same name exists in the given location, those files are overwritten.
The following command creates an SSH key pair using RSA encryption and a bit length of 4096:
If you use the Azure CLI to create your VM with the az vm create command, you can optionally generate SSH public and private key files using the --generate-ssh-keys option. The key files are stored in the ~/.ssh directory unless specified otherwise with the --ssh-dest-key-path option. If an ssh key pair already exists and the --generate-ssh-keys option is used, a new key pair will not be generated but instead the existing key pair will be used. In the following command, replace VMname and RGname with your own values:
Provide an SSH public key when deploying a VM
To create a Linux VM that uses SSH keys for authentication, specify your SSH public key when creating the VM using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, Azure Resource Manager templates, or other methods:
If you're not familiar with the format of an SSH public key, you can display your public key with the following cat command, replacing ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with the path and filename of your own public key file if needed:
A typical public key value looks like this example:
If you copy and paste the contents of the public key file to use in the Azure portal or a Resource Manager template, make sure you don't copy any trailing whitespace. To copy a public key in macOS, you can pipe the public key file to pbcopy. Similarly in Linux, you can pipe the public key file to programs such as xclip.
The public key that you place on your Linux VM in Azure is by default stored in ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub, unless you specified a different location when you created the key pair. To use the Azure CLI 2.0 to create your VM with an existing public key, specify the value and optionally the location of this public key using the az vm create command with the --ssh-key-values option. In the following command, replace myVM, myResourceGroup, UbuntuLTS, azureuser, and mysshkey.pub with your own values:
If you want to use multiple SSH keys with your VM, you can enter them in a space-separated list, like this --ssh-key-values sshkey-desktop.pub sshkey-laptop.pub.

SSH into your VM
With the public key deployed on your Azure VM, and the private key on your local system, SSH into your VM using the IP address or DNS name of your VM. In the following command, replace azureuser and myvm.westus.cloudapp.azure.com with the administrator user name and the fully qualified domain name (or IP address):
If you specified a passphrase when you created your key pair, enter that passphrase when prompted during the login process. The VM is added to your ~/.ssh/known_hosts file, and you won't be asked to connect again until either the public key on your Azure VM changes or the server name is removed from ~/.ssh/known_hosts.
If the VM is using the just-in-time access policy, you need to request access before you can connect to the VM. For more information about the just-in-time policy, see Manage virtual machine access using the just in time policy. Adobe photoshop 7 for mac free download.
Next steps
For more information on working with SSH key pairs, see Detailed steps to create and manage SSH key pairs.
If you have difficulties with SSH connections to Azure VMs, see Troubleshoot SSH connections to an Azure Linux VM.
This tutorial explains the Passwordless SSH using Public Key and Private Key in Linux.
SSH stands for Secure SHELL, is a protocol used to connect remote hosts to login or performing some tasks using scripts.
When we want to automate some tasks on remote hosts using scripts from a centralized server like Jenkins/Ansible or any Linux Server, we may require a password less connection between the remote hosts and the centralized Server.
In this tutorial, we will learn to create Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. Follow the step by step guide to make your ssh connection passwordless.
This tutorial will work for Linux Destro such as Centos, Ubuntu, Redhat, Amazon Linux(AWS EC2) and Other as well.
Recommended Read:How to Install Jenkins on Ubuntu
Also Read : Git Tutorial for beginners (Part I)
Scenario
We have one Local Machine and one Remote Server.We will setup a passwordless connection to login Remote Server from the local Machine.
Perform following steps on the remote Server
Step 1– Create an User and login or login as an existing user.
$ useradd devops
$ su – devops
Step 2 – Generate a key pair ( Public key and Private Key) using ssh-keygen command.
Before running this command make sure you are on home directory of the user.If not you can go to the home directory by cd ~ command. Astrology software for mac free download.
$ cd ~
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
It will ask for some details. Do not put anything here and press ENTER only.
By ls -al command you can see a hidden directory .ssh and two files namely id_rsa and id_rsa.pub inside .ssh directory are created.Here id_rsa is the Private key and id_rsa.pub is the Public Key.
Private key(id_rsa) is kept at source computer(local machine) from where you have to ssh. Public Key(id_rsa) is kept at Destination Server(Remote Server) , the Server you want to access.
Step 3- Create a file name authorized_keys in side .ssh directory and copy the content of id_rsa.pub file to authorized_keys file.
Go to .ssh directory
$ cd ~/.ssh/
Create an empty file name authorized_keys
$ touch authorized_keys
Copy the content of id_rsa.pub to authorized_keys
$ cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys
Ssh Public Key Authentication
Check the authorized_keys file if contents are copied.
$cat authorized_keys
Step 4 – Change the permission of authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 authorized_keys
Step 5– Copy the content of id_rsa file
Use cat command to display the content of id_rsa and copy its content.

$ cat id_rsa
On the local Machine
Step 1– Create a file and paste the content of id_rsa copied from remote server inside this file. You can use nano command to perform this action.
Create a file name devops.key using nano command , paste the content and pres Ctrl+X to save and close the file.
Use Public Key Ssh File
$ nano devopys.key
Step 2 – SSH remote Server from local machine without using password.
$ sudo ssh -i path-to-private-key [email protected]
$ sudo ssh -i devops.key [email protected]
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. If you think this is really helpful, please do share this to other as well. Please also share your valuable feedback, comment or any query in the comment box.I will really happy to resolve your all queries.
Thank You
Use Ssh Public Key With Putty
If you think we helped you or just want to support us, please consider these:-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter
